How Will the Joe Biden Tax Plan Affect Me?

Nov 10 | 2020
With the election of Joe Biden to the Presidency, you’re probably here seeking to understand how much your taxes are going to go up.
The answer: most people will see no tax increases.
The tax plan that Joe Biden has rolled out is targeted at individuals making more than $400,000 a year, less than 1% of the population of the US. If you (like me) are not one of these lucky individuals, then it’s very-likely that nothing in this article is going to apply to you.
But, for argument’s sake, let’s hop in the Model S, drive over to the penthouse, and analyze what Biden’s tax code plans mean for you.
If you make over $400,000 a year
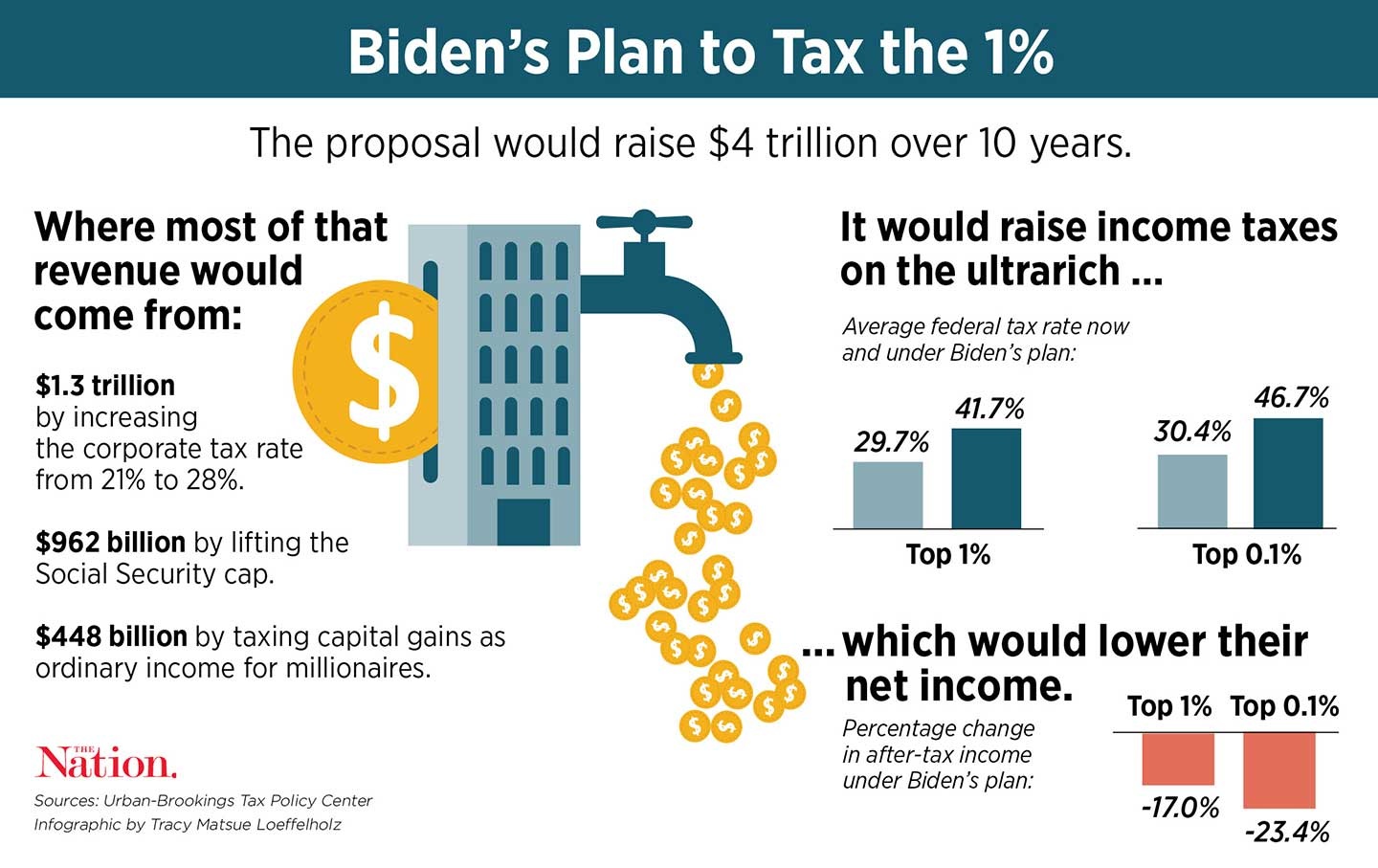
First, Biden is going to impose a 12.4% tax on incomes over $400,000 to fund Social Security, split evenly between employers and employees. This is a new tax, because Social Security taxes in the past have been capped on income at or below $137,700.
People who made over $137,700 had a tax break where they didn’t have to pay into Social Security for all of their income. Biden’s tax plan still allows people making over $137,700 to not pay the Social Security payroll tax for income above that amount as long as they make under $400,000.
When your income exceeds $400,000, you then have to start paying the tax again. This creates an interesting tax structure where people’s income at the very bottom and the very top of their income is being taxed for Social Security, but income in the middle is not.
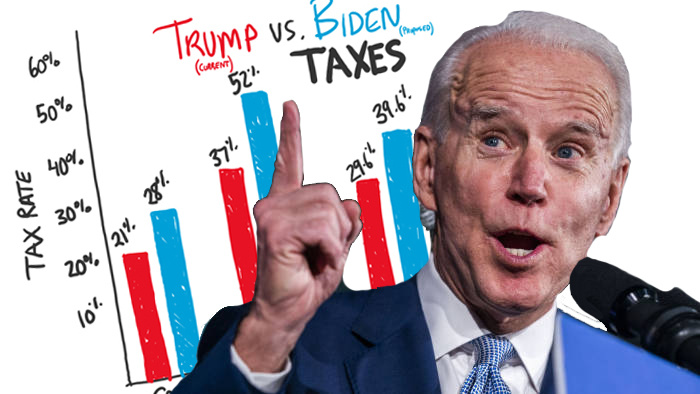
Second, while Biden is likely to keep many of changes from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, he has stated that he is going to revert the marginal tax rate for individual incomes above $400,000 from 37% back to the previous 39.6%. As with the Social Security tax, this does not kick in unless your income goes above $400,000.
Individuals making above $400,000 will also have their incomes above $400,000 see itemized deductions capped at 28%. That means if your income is over $400,000 and your tax rate is over 28%, you have less options for itemizing your deductions to get a lower tax rate.
Some business owners have benefitted from deducting up to 20% of their business income as well as 20% of the dividends from qualifying Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) on their taxes. Biden is proposing phasing that out for incomes above – drumroll – $400,000.
But what if you’re not just making $400,000 a year? What if you are making even more than $400,000 a year? What if you earn over $1 million a year? That’s when Biden’s really going to hit you where it hurts – your investments.
Most people pay taxes on what’s called “earned income,” referring to things like your salary at your job. The tax rates for that range from 10% to 37%, depending on how much you make. If you make money from investments instead, that’s a whole different story.
If you buy an investment and sell it for a profit within one year of purchase, you would pay your normal income tax on any profit you make. But if you hold the investment for longer than a year, you pay a reduced tax rate between 0% and 20%, depending on your income.
If you make over $200,000 ($250,000 for married couples), you would also pay a 3.8% tax on net investment income. What Biden is proposing is taxing any income over $1 million the same regardless of it comes from your salary or your long-term investments.
The wealthiest people in the US have seen a large amount of their income come from investments, and this measure would keep the wealthiest Americans from paying less in taxes than average working people just because the money comes from holding stocks or real estate instead of a traditional job.
If you make under $400,000 a year
Let’s say that you, like more than 99% of Americans, do not make $400,000 a year. Does this mean Biden’s tax plan will not affect you at all? There’s actually a decent chance you might see some changes to your taxes.
Biden is proposing bringing back the First-Time Homebuyers’ Tax Credit, originally created to help the housing market during the Great Recession, and provide up to $15,000 for first-time homebuyers. With interest rates at historic lows, this may be another incentive for you to consider dipping your toes into the real estate game and becoming a homeowner.
Biden is also proposing expanding the Child and Dependent Care Tax Credit from $3,000 up to $8,000 for one dependent and $16,000 if you have multiple dependents. The maximum reimbursement rate would also adjust from 35% to 50%. If you have kids or other dependents, this may reduce how much you pay in taxes by giving you a child tax credit the money you spend to support your family.
Biden also has a few very targeted tax cuts and tax benefits that will apply to a much smaller group of people. One is expanding the Earned Income Tax Credit (a tax credit for low-income people who are very close to the poverty line) and allowing people over the age of 65 to also claim the credit even if they do not have dependent children.
He would also provide a refundable low-income renter’s credit, reinstate tax credits for the purchase of electric vehicles and improvements to your home to make them more energy-efficient, as well as exempt forgiven student loans from taxable income. These may not apply to as wide a group of people, but if you’re older, a renter, looking to live a more green lifestyle, or seeking forgiveness for student loans, Biden’s tax proposals can have you looking at a smaller tax bill.
Biden’s plans for inheritances
At first glance, it looks like everyone making more than $400,000 a year will pay higher taxes and everyone else will pay less taxes than they currently do. However, there is a part of Biden’s tax plan that may have an impact on you even if you are lower income – if you have a rich family.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act raised the threshold at which estate taxes are paid and lowered how much they have to pay in taxes. If you stand to inherit an estate worth $11.6 million dollars today ($23 million if you are a married couple), right now you don’t pay taxes on it.
If you inherit more than that, you would pay a top rate of 40% tax. Biden is proposing lowering the threshold where the tax would kick in back down to $3.5 million ($7 million for married couples) and raising the tax rate back to 45%. This will affect roughly 0.3% of estates. If you are in the 99.7%, you do not need to worry about the Biden inheritance policy.
Now, the next part is closing an inheritance loophole called the “stepped-up basis” loophole. Right now, when an heir inherits an asset, they only pay taxes on the gain in value of the asset from the time that they inherited it.
Let’s say your parents bought $100 worth of stocks decades ago and today those stocks are worth $10,000. If your parents passed away and left you the stocks, you would be allowed to sell them immediately and not pay any taxes.
If you held the stock and the price rose to $12,000, you would only pay taxes on the $2,000 in value the stocks gained since you inherited it. This because the initial value of the stocks would be “stepped-up” to the value at the time you inherited it rather than the value at the time your parents bought it.
This loophole has allowed the very wealthy to leave very valuable assets to their children without needing to pay taxes and allowed generations to pass large fortunes to their children. Biden has proposed closing this loophole and not stepping-up the value of an asset when it is inherited; taxes will instead be paid on the value of the asset from when it was first purchased.
This part of the plan has yet to be fully fleshed-out by Biden, but it appears to be modelled after a proposal from the Obama administration. That plan allowed an exclusion of $100,000 per person (rising with inflation) and excluding $250,000 for primary residences ($500,000 for couples). It also allowed a 15-year payment period and tax deferrals for family-owned small businesses. Biden may roll out similar provisions once he rolls his tax plan out before congress.
Does any of the Biden tax policy outlines even matter?
Maybe?
Biden has presented something of a wish list for his tax plan, but that doesn’t mean he can wave a magic wand on January 20th and put it into place. This plan will require significant negotiations in Congress, and if Republicans retain a Senate majority, they may refuse to even allow a bill to have a hearing. Ultimately, Biden’s tax proposals may change significantly as they work their way through Congress and if they are not able to garner enough support, they may never come into effect.